This Excel tutorial serves as the ultimate guide to mastering age calculation in Excel. Whether you’re working with people, objects, business assets, commercial projects, or insurance records, learning how to calculate age in Excel is essential.
When calculating the age of individuals or items, the key is bridging the gap between two dates. For humans, this often starts with their date of birth (DOB). Another approach is projecting the aging of individuals or objects to a future timeframe.
Yet, such calculations involve navigating dates, especially the complexities tied to varying days in months. This is where Excel’s age calculation techniques come to your aid. Moreover, by learning the methods outlined in this article, you’ll be able to compute the age of thousands of subjects within seconds.
Here’s why you must master the skills of various types of age calculations in Excel:
At the time of writing, the latest Excel desktop app is the Excel for Microsoft 365 and there’s no dedicated commands block for age calculation on the Excel Formulas tab. Neither, there are any direct formulas to calculate age in Excel.
However, you can make use of various other functions in Excel that calculate dates. So, when you’re following the manual method of solving for age or aging in Excel, you must remember some formulas that can help.
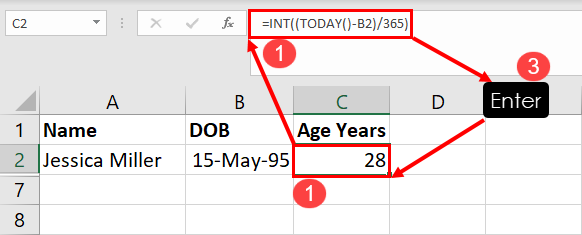
The easiest combination of an Excel formula and the mathematical operator division to calculate age is TODAY() and dividing the time to date by 365 to get a rough age of a person or object. However, you must also need a date of birth for human beings and starting date for objects or projects.

Here’s how you can calculate age when the DOB or start date is given:
=INT((TODAY()-B2)/365)Another Excel function you can use to calculate the age of people or things from a start date and end date is the YEARFRAC formula.
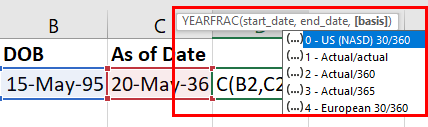
The formula enables you to input an argument so Excel understands the day count basis you want to use. For example, you can use the numbers 0 to 4 to indicate US (NASD) 30/360, Actual/Actual, Actual/360, Actual/365, and European 30/360 respectively.
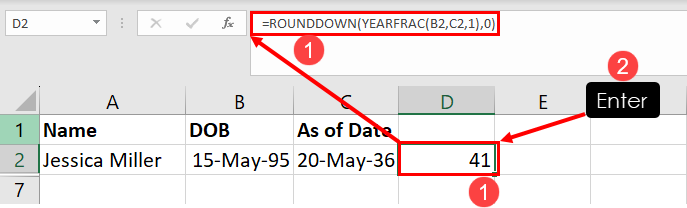
Here’s how you can use this function to calculate project length between two dates or the age of a person between the DOB and a specific date:
=ROUNDDOWN(YEARFRAC(B2,C2,1),0)In the above formula, B2 is for the start date or DOB and C2 represents the specific date up to which you want to calculate age or project length. So, customize the formula according to your own worksheet.
The methods mentioned so far only calculate the age in complete years. What if you need the age in years, months, and days? In this situation, you use a nested formula of DATEDIF and IF with commas to separate each value and define the values as years, months, and dates.
The IF function ensures you don’t get 0 values like 0 years, 0 months, 0 days, etc. Thus, the resulting values read well and the dataset stays compact.
Find below the syntax you can use and the instructions for formula customizations:
=IF(DATEDIF(B2, C2, "y") > 0, DATEDIF(B2, C2, "y") & " years ", "") & IF(DATEDIF(B2, C2, "ym") > 0, DATEDIF(B2, C2, "ym") & " months ", "") & IF(DATEDIF(B2, C2, "md") > 0, DATEDIF(B2, C2, "md") & " days", "")Here’s how you can customize the above formula:
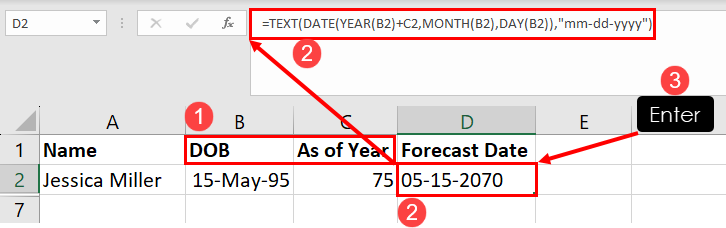
Using Excel, you can easily forecast the date when a person will attain N years of age. Suppose, your friend’s DOB is 15-May-95. Now, you’d like to know when will she turn 75. Use the following formula and follow along with the steps to practice:
=TEXT(DATE(YEAR(B2)+C2,MONTH(B2),DAY(B2)),"mm-dd-yyyy")In the above formula, B2 represents the start date or DOB and C2 represents the age of a person or the span of a project in years.
Suppose, you don’t want to perform all these clicks or remember functions to calculate age in Excel. In that scenario, you can use Excel VBA to write a script and automate the whole process.
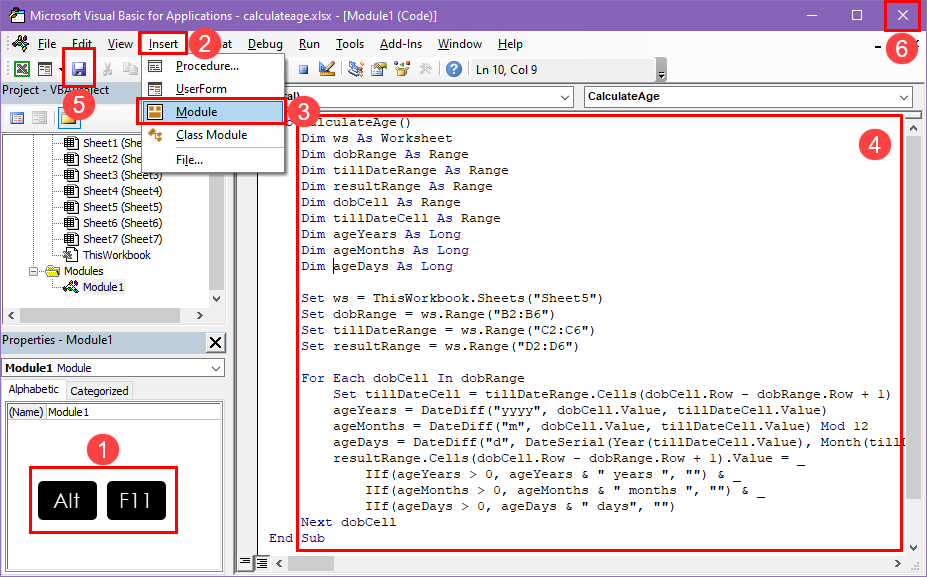
Don’t know how to write an Excel VBA script to calculate age in Excel? No issues! Find below a handy script you can use right away. For your assistance, I’ve also mentioned the steps you can follow:
Sub CalculateAge() Dim ws As Worksheet Dim dobRange As Range Dim tillDateRange As Range Dim resultRange As Range Dim dobCell As Range Dim tillDateCell As Range Dim ageYears As Long Dim ageMonths As Long Dim ageDays As Long Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet5") Set dobRange = ws.Range("B2:B6") Set tillDateRange = ws.Range("C2:C6") Set resultRange = ws.Range("D2:D6") For Each dobCell In dobRange Set tillDateCell = tillDateRange.Cells(dobCell.Row - dobRange.Row + 1) ageYears = DateDiff("yyyy", dobCell.Value, tillDateCell.Value) ageMonths = DateDiff("m", dobCell.Value, tillDateCell.Value) Mod 12 ageDays = DateDiff("d", DateSerial(Year(tillDateCell.Value), Month(tillDateCell.Value), 1), tillDateCell.Value) resultRange.Cells(dobCell.Row - dobRange.Row + 1).Value = _ IIf(ageYears > 0, ageYears & " years ", "") & _ IIf(ageMonths > 0, ageMonths & " months ", "") & _ IIf(ageDays > 0, ageDays & " days", "") Next dobCell End Sub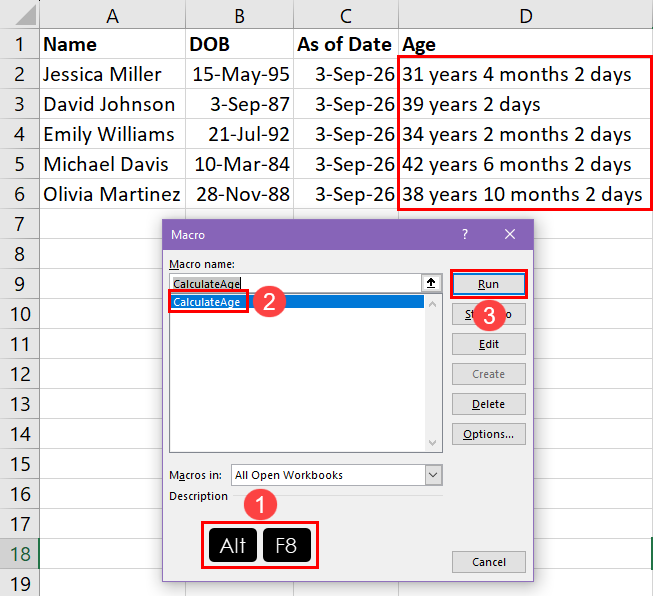
So far, you’ve created a VBA macro. Now, learn below how to execute the script:
Find below the instructions to customize the VBA script:
Another advanced automation method in Excel is Office Scripts. Like Excel VBA, this feature allows you to write scripts in TypeScripts language to instruct Excel to perform data analysis automatically. An advantage of this feature is it works in both Excel for Microsoft 365 desktop and Excel for the web app.
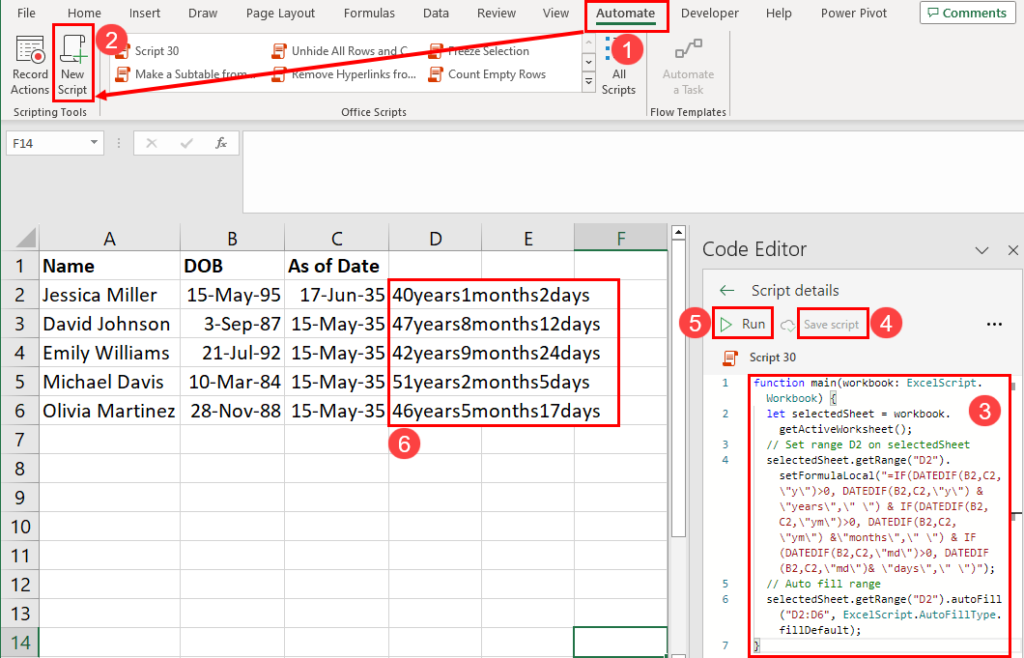
Find below an Office Scripts code to calculate age in years, months, and days from date of birth and as of date:
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) < let selectedSheet = workbook.getActiveWorksheet(); // Set range D2 on selectedSheet selectedSheet.getRange("D2").setFormulaLocal("=IF(DATEDIF(B2,C2,\"y\")>0, DATEDIF(B2,C2,\"y\") & \"years\",\" \") & IF(DATEDIF(B2,C2,\"ym\")>0, DATEDIF(B2,C2,\"ym\") &\"months\",\" \") & IF(DATEDIF(B2,C2,\"md\")>0, DATEDIF(B2,C2,\"md\")& \"days\",\" \")"); // Auto fill range selectedSheet.getRange("D2").autoFill("D2:D6", ExcelScript.AutoFillType.fillDefault); >Find below the quick tips to customize the above script to fit your Excel worksheet and its datasets:
📝 Note: The availability of Office Scripts depends on the Microsoft 365 subscription you or your company is using. If your subscription is Business Standard or better, you’ll find the feature in Excel on the web. For the Excel desktop app, you must download the Excel for Microsoft 365 app from the Microsoft 365 Home portal.
This post has explored three different Excel formulas to calculate age in Excel from date of birth or a start date, when it’s a project or business asset.
Also, you explored two different automation methods, Excel VBA and Office Script, to automate the task in Excel.
Follow along with the steps using your own dataset. Don’t forget to comment below to share your thoughts, suggestions, or experience while trying out the above methods.
I'm a freelance writer at HowToExcel.org. After completing my MS in Science, I joined reputed IT consultancy companies to acquire hands-on knowledge of data analysis and data visualization techniques as a business analyst. Now, I'm a professional freelance content writer for everything Excel and its advanced support tools, like Power Pivot, Power Query, Office Scripts, and Excel VBA. I published many tutorials and how-to articles on Excel for sites like MakeUseOf, AddictiveTips, OnSheets, Technipages, and AppleToolBox. In weekends, I perform in-depth web search to learn the latest tricks and tips of Excel so I can write on these in the weekdays!
Subscribe for awesome Microsoft Excel videos 😃
👉 Find out more about our Advanced Formulas course!